
[派瑞林日記]我可以加紫外熒光劑到派瑞林涂層嗎?
三防漆和紫外熒光劑
三防漆通過各種操作環境為印刷電路板(PCB)和類似電氣組件提供出色的保護,保護其化學,電氣和/或機械性能。
涂層的可靠性根據涂層材料和使用條件而變化。如果要將PCB直接暴露在紫外線下,大多數三防漆都需要專門的加工和檢驗程序。肉眼看不見,紫外線輻射的波長在100-400納米(nm)之間。向涂層中添加UV通常熒光劑用于液體保形涂料中以用于檢查目的,但是對于聚對二甲苯使用具有顯著的缺點。
Parylene一再表現出卓越的實用性,超越了大多數競爭性涂料(包括丙烯酸,環氧樹脂,硅樹脂和聚氨酯)作為生物,消費品,工業,醫療和軍事系統基材的性能,包括:納米防水網:http://www.yctpl.com/
·對部件形狀的適應性,
·介電強度,
·耐用,靈活的部件保護,
·絕緣性能,
·無針孔均勻涂層,
·耐化學品和溶劑。
此外,與競爭對手相比,聚對二甲苯涂層可以以超薄層施加,在最終產品上通常不會檢測到厚度水平的顯著保護。
聚對二甲苯和紫外線
盡管其作為保形涂層具有許多應用和特性,但大多數聚對二甲苯品種對UV輻射的總體耐受性是有限的。雖然在室內保持穩定,但大多數聚對二甲苯配方不建議在直射陽光下長期操作環境下使用。
也就是說,聚對二甲苯C和N的UV穩定性很少超過100小時; 聚對二甲苯AF-4在這方面是優越的,當按照現行的ASTM G 154標準進行測試時,提供2,000小時或更長時間的紫外線防護。這種性能水平還超過了由丙烯酸,環氧樹脂,硅樹脂和聚氨酯制成的競爭性保形涂層。
紫外熒光劑和聚對二甲苯
在大多數液體保形涂層處理的檢查階段使用UV熒光劑。但是,在聚對二甲苯涂層的情況下,必須注意以下原因:
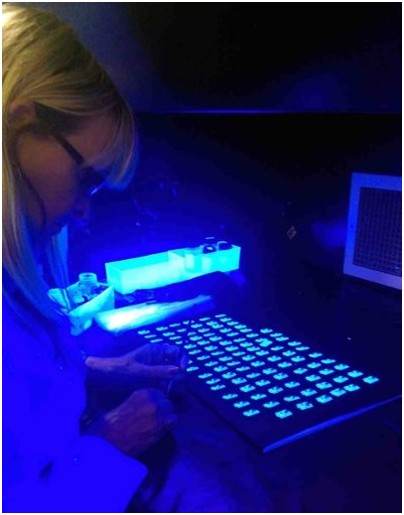

·UV微量添加劑不是聚對二甲苯二聚體的一部分,必須在涂覆前加入。
·紫外熒光材料的分子結構大于聚對二甲苯分子。
·Parylene材料保留了滲透掩蔽的能力,三十UV熒光劑不能滲透。
·因此,粗略檢查可能無法檢測無涂層區域內的UV材料。
·該組件可以通過檢查,授權和清除其設計的功能,即使這些缺陷未被檢測到。
常包括均勻的熒光劑,但是聚對二甲苯不具有。在UV光檢測期間,UR,AR和SR涂層發出明亮而清晰的熒光。它們清楚地表明了痕跡在涂層中的精確位置,在涂層中已經存在并且尚未應用。
在這些情況下,假定向聚對二甲苯二聚體中添加UV熒光正確地指示涂層是否滲透到任何無涂層區域是錯誤的。
·在沉積過程中,UV熒光劑往往會隨機濺到PCB或其他組件上。
·在某些情況下,UV熒光劑的不均勻支付可能導致材料隨意劃傷。
·無論是否采取措施減輕這些可能性,其他PCB都可能完全沒有紫外熒光劑。
通過基于這些不可靠結果的檢查來通過組件不僅會導致組件故障,而且還會導致潛在的危險結果,其中通過堅固耐用或類似的專業操作條件來依賴組件以獲得可靠的性能。
紫外固化和聚對二甲苯
用于保護保形涂料,粘合劑和油墨的光化學工藝,與常規固化技術相比,UV固化產生各種增值性能。將高強度紫外線照射到干燥(固化)涂層或其他物質上,紫外線固化可以提供即時效果,提高生產速度,同時減少對典型設置和清理過程的需求和數量。降低的操作成本和增加的生產能力是許多涂料和工藝的UV固化的進一步優點。
在這些情況下,涂層和基材之間的優異粘合是環保的,節省能源而無需排放控制。過程/產品拒絕的發生率降低提供了以下額外的好處:
·更好的附著力和粘合強度,
·耐用而有彈性的涂層表面,
·增強耐磨性/表面劃傷性,
·具有更好的防止接觸化學品和溶劑的保護。
在程序上,UV固化過程中必不可少的光化學反應將液體單體和低聚物與微量痕量的光引發劑混合,光引發劑隨后暴露于UV能量。在紫外線固化過程中,紫外線與特殊配方的化學物質相互作用,比傳統方法更快地固化涂層。光引發劑吸收來自處理光源的紫外線能量,無論是弧光還是激光。所得到的化學反應在幾秒鐘內將液體涂料配方轉化為穩定的固化膜。
在沉積聚對二甲苯之后,如果存在任何掩蔽區域,則去除掩蔽材料。去掩蔽區域周圍的聚對二甲苯薄膜通過去掩蔽過程最小程度地損壞是相當普遍的。這可能導致聚對二甲苯的“手指”或甚至大的撕裂。有時,創建的邊緣必須密封,以防止任何濕氣或其他化學物質滲入側邊的可能性。
可以通過施加液體保形涂層來修復這些邊緣或其他缺陷。我們經常使用聚氨酯保形涂料,因為它最接近地顯示聚對二甲苯的性質。有時我們的客戶會要求我們使用UV固化液體修飾材料。但是,由于上述原因,我們不建議使用任何與聚對二甲苯涂層配合使用的UV固化機制,因為它會嚴重降低薄膜的性能。
盡管有效用于其目的,但這種方法與聚對二甲苯的化學氣相沉積(CVD)工藝很大程度上不相容,嚴重限制了其與聚對二甲苯的適用性。
總 結
不推薦使用UV熒光劑和UV固化材料作為LED器具的聚對二甲苯敷形涂料的組分。
最重要的是要了解UV熒光劑不是原始聚對二甲苯二聚體的一部分。由于這種現實,組合這兩種材料改變了沉積的保形涂層的組成,污染了聚對二甲苯的純度。隨后的聚對二甲苯-UV熒光劑雜化物可以通過檢查,但通常不會比其它情況下更耐UV光。同時,由于引入了UV熒光劑污染物,因此使用聚對二甲苯保形涂層的基本導電,絕緣和保護性能將會降低。
絕對沒有數據支持這種混合薄膜的任何改進性能,并且由于污染物的引入,UV熒光劑很可能最終會嚴重降低聚對二甲苯的性能。盡管如此,目前的證據表明,盡管大多數聚對二甲苯類型(C,D,N)的容量有限,無法為暴露于紫外光源的LED提供可靠的長期保護,但已設計出可用于外部LED使用的聚對二甲苯涂層。與UV熒光劑一樣,對于聚對二甲苯是優選的保形涂層材料的眾多應用中的任何一種,UV可固化涂層是組合的不良選擇; 因此,它不應該用于涂抹聚對二甲苯。
英文原文
Conformal Coatings and UV Trace
Conformal coatings provide exceptional protection for printed circuit boards (PCBs) and similar electrical assemblies, through a wide variety of operating circumstances, safeguarding their chemical, electrical, and/or mechanical properties.
The reliability of coatings varies according to the coating material and conditions of use. Most conformal coatings require specialized processing and inspection procedures if PCBs are to be used in direct exposure to UV light. Invisible to the naked eye, UV radiation’s wave length registers between of 100-400 nanometers (nm). The addition of UV trace to coatings is commonly used in liquid conformal coatings for inspection purposes, but has significant drawbacks for parylene use.
Unsuitably of UV Treatments for Parylene Conformal Coatings
Parylene has repeatedly demonstrated superior utility in comparison to most competitive coatings – including acrylic, epoxy, silicone and urethane -- surpassing their performance as a substrate covering for biological, consumer, industrial, medical and military systems, in terms of:
· adaptability to component shape,
· dielectric strength,
· durable, flexible component protection,
· insulating properties,
· pinhole-free uniform coating, and
· resistance to chemicals and solvents.
In addition, parylene coatings can be applied in ultra-thin layers, compared to competitors’, providing significant protection at thickness levels are generally undetected on the final product.
Parylene and UV Light
Despite its many applications and assets as a conformal coating, the overall resistance of most parylene varieties to UV radiation is limited. While it remains stable indoors, most formulations of parylene are not recommended for long term use outdoors where exposure to direct sunlight is a condition of the operating environment.
That is, the UV stability of parylenes C and N seldom exceeds 100 hours; parylene AF-4 is superior in this respect, providing UV-protection for 2,000 hours or more, when tested according to the prevailing ASTM G 154 standards. This level of performance also exceeds competing conformal coatings produced by acrylic, epoxy, silicone and urethane.
UV Trace and Parylene
UV trace is used during the inspection stage of most liquid conformal coating processing. However, in the case of parylene coatings, care must be taken for the following reasons:

· The UV trace additive is not part of the parylene dimer and must be added prior to coating.
· The molecular structure of UV fluorescent materials is larger than that of parylene molecules.
· Parylene materials retain the ability to penetrate masking, even where those of UV fluorescents do not.
· Thus, cursory inspection may not detect UV material within the coating-free zone.
· The component may pass inspection, authorized and cleared for functions it is designed for, even as these flaws go undetected.
This is a problem for application of parylene coatings, in comparison to competitive conformal types, when a UV tracer is added. For instance, while urethane (UR), acrylic (AR) and silicone (SR) typically include a uniform fluorescing agent in their chemistry, parylene does not. During UV light inspection, UR, AR and SR coatings fluoresce brightly and clearly. They plainly indicate the precise location of the trace within the coating, where it has and has not been applied.
Under these circumstances, it is wrong to presume the addition of a UV florescent to the parylene dimer correctly indicates whether or not the coating has infiltrated any coating free zones.
· The UV trace tends to randomly splatter onto PCBs or other assemblies during its deposition process.
· Uneven disbursement of the UV trace can cause haphazard streaking of the material in some instances.
· Other PCBs may receive no UV trace at all, regardless of the care taken to alleviate these possibilities.
Passing the component through inspection based on these unreliable outcomes can not only lead to component malfunction, but also potentially dangerous outcomes, where the component is relied on for reliable performance through ruggedized, or similarly specialized, operating conditions.
UV Curing and Parylene
A photochemical process used to preserve conformal coatings, adhesives, and inks, UV curing generates a variety of value-added properties in comparison to conventional curing techniques. Applying high-intensity UV light to dry (cure) coatings or other substances, UV curing can provide instant results, increasing production speed while reducing the need for and number of typical set-up and clean-up processes. Lowered operating costs and increased production capacity are further advantages of UV curing for many coating materials and processes.
In these cases, the consequent superior bonding between coating and substrate is environmentally friendly, saving energy without need for emissions’ controls. The diminished incidence of process/product rejection offers the additional benefits of:
· better adhesion and bond strength,
· durable yet elastic coating surfaces, and
· enhanced resistance to abrasion/surface scratching,
· with improved protection against exposure to chemicals and solvents.
Procedurally, the photochemical reaction essential to the UV curing process mixes liquid monomers and oligomers with minute traces of photoinitiators, which are subsequently exposed to UV energy. In the UV curing process, ultraviolet light interacts with specially formulated chemistries to cure coatings more rapidly than possible with traditional methodologies. The photoinitiators absorb the UV energy from the process light source, either arc light or laser light. The resultant chemical reaction converts liquid coating formulation into a stable, cured film in a matter of seconds. 納米防水網:http://www.yctpl.com/
After parylene has been deposited, if there were any masking areas, the masking materials are removed. It is fairly common for the parylene film around the de-masking area to be minimally damaged by the de-masking process. This can result in “fingers” of parylene or even large tears. Sometimes, it is critical that the edges that were created be sealed to prevent any possibility of moisture or other chemicals penetrating the side edges.
These edges or other imperfections can be repaired via the application of a liquid conformal coating. We often use urethane conformal coating, as it most closely exhibits the properties of parylene. Sometimes our customers will request that we use a UV curable liquid touchup material. However, for the reasons outlined above, we do not recommend using any UV curing mechanism in concert with parylene coating, as it can severely degrade the film.
While efficient for its purposes, this approach is largely incompatible with parylene’s chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process, severely limiting its suitability for use with parylene.
Summary
Applying UV trace and touching up with UV cured material as components of parylene conformal coatings for LED appliances is not recommended.
Of paramount importance is understanding that the UV trace is not part of the original parylene dimer. Because of this reality, combining the two materials changes the composition of the deposited conformal coating, tainting the purity of the parylene. The consequent parylene-UV trace hybrid may pass inspection, but will typically not be any more resistant to UV light than it would otherwise have been. At the same time, the conductive, insulating and protective properties basic to the use of parylene conformal coatings will be diminished because of the introduction of UV trace contaminants.
Absolutely no data supports any improved properties of this hybrid film and, as a result of the introduction of the contaminant, it is highly likely that UV trace will ultimately degrade the parylene's performance, potentially in a serious way. Nevertheless, the current evidence shows that, despite the limited capacity of most parylene types – C, D, N – to provide dependable, longer-term protection for LEDs exposed to UV sources, parylene coatings have been devised that are useful for external LED use. As with UV trace, UV curable coating is a bad choice for combination for any of the numerous applications where parylene is the preferred conformal coating material; thus, it should not be used for touch up with parylene.

隨著電子產品防水需求的不斷提高,從原先的 IP54到現在的IP67IP68等級!市場上出現了防水透氣膜和防水透音膜,目前這兩種不同的材料應用被搞混了,今天便與大家一起討論防水透氣
最近各地降雨量激增,所以手機就難免會沾點水,作為生活中不可或缺的電子產品,防水已經成為一個十分重要重要功能,而且個人對目前的IP68手機市場是相當不滿意的。為什么?太貴
自然界中荷葉具有出淤泥而不染的典型不沾水特性(學術上稱為Cassie-Baxter狀態),具有自清潔、抗結冰、減阻、抗腐蝕等廣泛應用價值,而玫瑰花瓣則具有水滴高粘附特性(稱為Wenze

派瑞林各種粉材真空鍍膜技術加工 納米涂層防水處理
派瑞林各種粉材真空鍍膜技術加工 納米涂層防水處理

高阻隔強絕緣防汗液涂層藍牙耳機3C電子產品IPX7納米材料
高阻隔強絕緣防汗液涂層藍牙耳機3C電子產品IPX7納米材料

耐磨超疏水納米材料 絕緣子架空導線電纜橋梁防覆冰涂層
耐磨超疏水納米材料 絕緣子架空導線電纜橋梁防覆冰涂層

真空等離子氣相沉積技術納米防水鍍膜加工 產能5萬片天
真空等離子氣相沉積技術納米防水鍍膜加工 產能5萬片天
親水疏油自潔凈納米涂層 易去污 無機防紫外高硬度材料
親水疏油自潔凈納米涂層 易去污 無機防紫外高硬度材料

臺灣超親水防霧塑料專用 附著力好 透過率高 持久有效
臺灣超親水防霧塑料專用 附著力好 透過率高 持久有效

